“Thermorheological and mechanical behavior of polylactide and its enantiomeric diblock copolymers and blends”
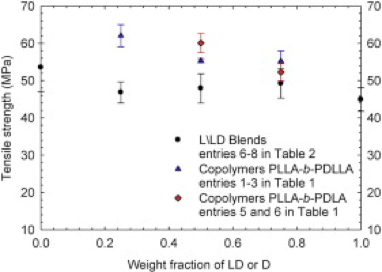
In this study, different compositions of nearly monodispersed diblock copolymers of DL-lactide or D-lactide and L-lactide were synthesized by living ring-opening polymerization with a dinuclear indium catalyst. The effects of molecular weight and block length ratio on the rheological behavior of DL and L-lactide diblock copolymers in the disordered state were investigated. For comparison, blends of PDLLA and PLLA homopolymers of equivalent molecular weights to the diblock copolymers were prepared. We found that the time-temperature (t-T) superposition principle is applicable to the diblock copolymers PLLA-b-PDLLA and blends in the disordered state. However, the t-T superposition failed at low temperatures close to the temperature of crystallization. In contrast, diblock copolymers PLLA-b-PDLA formed stereocomplex crystallites of high melting point (slightly above 200 C) that causes a viscosity enhancement. The failure of t-T superposition was found due to existing of micro homo or stereocomplex crystallites. The non- isothermal crystallization behavior was investigated using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The DSC thermograms of blends exhibited a single glass transition at 50-60 C followed by melting point of PLLA at 177 C. With decreasing of the PLLA content in the blends, the intensity of the melting peak decreased. In addition, different crystallization behavior was observed for diblock copolymers compared to their equivalent blends. Specifically, low temperatures and enthalpies of melting peaks were observed for diblock copolymers. These also show improvement in elongation at break and tensile strength as compared to their counterpart homopolymer blends.